Blazor Interview Questions and Answer
Before getting into this article, we would suggest you please read all our other Blazor articles for more and sequential information about ASP .NET Core Blazor with the links below:
- Chapter 1: Blazor Interview Questions and Answers
- Chapter 2: What is ASP.NET Core Blazor?
- Chapter 3: Blazor Vs Angular
- Chapter 4: Blazor hosting models
- Chapter 5: Project Structure in Blazor
- Chapter 6: What are Blazor Components
- Chapter 7: net core razor components in details | Nesting Razor Components
- Chapter 8: Blazor Model Classes
- Chapter 9: Data Bindings in Blazor
- Chapter 10: Data access technique in blazor
Question 1: What is Blazor?
Answer: It’s a super awesome framework by Microsoft for building interactive client-side web UI with the best performance ever in .NET and C# named Blazor. In Blazor We use component-based architecture like other modern web development frameworks Angular or React.

Question 2: Type of Blazor?
Answer: Microsoft is offering Blazor in two types, as:
- Blazor Server
- Blazor Web Assembly
Question 3: What is Blazor Server?
Answer: Microsoft Blazor Server decouple the application layers as Blazor Components (in form of Razor component) with the support of C# to write the logic for the client browser. Blazor built on the top of the ASP.Net Core framework. It provides support for hosting Razor components on the server in an ASP.NET Core app. Blazor uses the SignalR for making a connection in the ASP.Net server to the DOM at Client Side.
Question 4: What is Blazor Web Assembly (WASM)?
Answer: Microsoft Introduced Blazor WebAssembly as a new way to use ASP.NET core at the client-side. This is in preview edition till now (March 2020). Blazor WebAssembly is a nice and clean way to create a single-page app for building interactive client-side web apps with the power of C# on client-side too, means on the browser with the uses of open web standards without any plugins or code transpilation.
Question 5: What is Web Assembly (WASM)?
Answer: According to “WebAssembly.org”: WebAssembly (abbreviated WASM) is a binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. WASM is designed as a portable target for compilation of high-level languages like C/C++/Rust, enabling deployment on the web for client and server applications.

Question 6: What are the Features of Blazor?
Answer: Blazor is much inspired by the other new and Morden UI Frameworks with many features. It’s not a replacement of any other JavaScript-based UI Frameworks, but yes it could be the best way for all the .Net Developer for creating next application with the list of rich features, as follows:
- Component-based architecture.
- DI (Dependency Injection.
- Blazor Forms and Validation.
- Live Reload.
- JavaScript interop.
- Unit Testing.
Question 7: What are the Supported Browsers for Blazor?
Answer: Blazor WebAssembly
|
Browser |
Version |
|
Microsoft Edge |
Current |
|
Mozilla Firefox |
Current |
|
Google Chrome, including Android |
Current |
|
Safari, including iOS |
Current |
|
Microsoft Internet Explorer |
Not Supported |
Blazor Server
|
Browser |
Version |
|
Microsoft Edge |
Current |
|
Mozilla Firefox |
Current |
|
Google Chrome, including Android |
Current |
|
Safari, including iOS |
Current |
|
Microsoft Internet Explorer |
Current |
Question 8: What is the component in Blazor?
Answer: Blazor uses the Razor template engine that generates HTML and serves to the web browsers. We can use both HTML and C# syntax all together in the Razor templates and Razor engine then compiles the Razor templates to generate the HTML. In Blazor Components we can use In-Line coding for the logics or we can separate it and can write the component functions into a separate C# class file. We use @code {} block for writing the C# functions along with HTML.
Blazor uses the “. razor” extension for Component identification.
Question 9: What are the differences between Blazor Server and Blazor WASM?
Answer:
|
Blazor WebAssembly |
Server-side Blazor |
|
The workload is distributed to each user. |
The server is responsible for resources. Like, SignalR instances. |
|
Browser dependency. |
No Browser dependency. |
|
Limited Access to .Net Assembly. As it’s work with a mono implementation that supports the majority of .NET Standard 2.0 APIs. |
Full Support at runtime of .Net Assembly. As it’s work on .Net Core Server. |
|
On the first request, All the DLLs will be loaded |
All the DLLs will remain on the server only and executed and secure on the server. Only UI will be updated, and the updates are exchanged with the client, using SignalR. |
|
Full support for Offline with progressive web applications (PWA). |
No support for offline mode. It’s Requires an active network connection for the client interactions. |
|
Full support for a content delivery network (CDN). So, can be hosted as a static website and served from CDN. |
Requires an active server that supports ASP. NET to function. |
|
Require low latency networks. Because most of the functions are executed on the client only. |
Relies heavily on server-side communication for rendering. |
|
Thick client. Due to more assemblies at the browser, the first request download size is big. |
Thin client. No assemblies required to be downloaded at the browser, so page size is very less. |
Question 10: What are the Pros and Cons of Blazor Server?
Answer: Blazor Server Pros:
- Page download size is very less.
- Full support of .Net assemblies as you are using Dot Net core at the server.
- Debugging like a boss.
- Run-on any browser.
- No need for JavaScript.
- Much secure, Code will be on Server only.
Blazor Server Cons:
- No Offline support always needs an active server.
- High latency network for server interactions.
- More resources are required for managing SignalR instances.
Question 11: What are the Pros and Cons of Blazor WebAssembly?
Answer: Blazor WebAssembly Pros:
- Low latency Network
- No Need for JavaScript understandings for client-side interactions.
- Offline support.
Blazor WebAssembly Cons:
- Page download size is big.
- Browser dependency, Internet Explorer not supported.
- Limited support of .Net Assemblies.
- Debugging is not so good at the client-side.
- Not so secure, DLLs will be download at the browser.
Question 12: What are the steps to create and run the Blazor Server App using CLI commands?
Answer: We can open the command prompt and type following command to create a Blazor server app using asp.net core CLI:
dotnet new blazorserver -o WebApplication1
cd WebApplication1
dotnet runQuestion 13: What are the steps to create and run the Blazor WebAssembly App using CLI commands?
Answer: We can open the command prompt and type following command to create a blazor WebAssembly app using asp.net core CLI:
dotnet new blazorwasm -o WebApplication1
cd WebApplication1
dotnet runQuestion 14: How to define a route in Blazor?
Answer: Using @page directive we can define a route for blazor components. Now, we can create a new Blazor Component and at the top of the HTML of this blazor component, add simply @page 'path', like this:
@page '/'This is for the home page or for those requests there is no URL parameter after domain but suppose we want to open new component and URL must be like 'https://domain/counter' so just add like this:
@page '/counter'Question 15: Data Binding in Blazor.
Answer: Bindings are the main thing to interact with the data or control object like Textboxes, Selects, or Forms elements, and here in this war of being the best Web Development framework, Blazor giving the tough competition to other modern Web development frameworks. Blazor comes with the best way to use bindings with One-way, Two-way Data Binding, and with the rich behavior of event binding.

Question 16: How to do Two-way Data Binding in Blazor?
Answer: Two-way data binding is the by directional data flow, means in this case the information flows in both directions, Source to Destination and Destination to Source at the same time like, we use the data variables of my component class(es) as a source and we need to get the value of this variable on the HTML UI to display some messages or edit them.
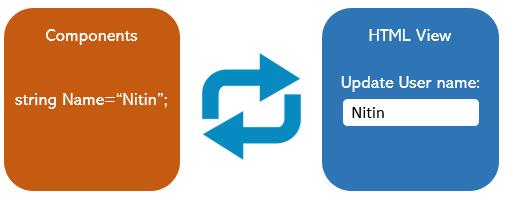
In Blazor we have @bind from razor to read the value of any Blazor component’s data variable. @bind gets the value from the ref and holds it when user changed the data and leaves the focus, it updates the original source element.
@code {
public string data { get; set; } = "Default Text";
}
<input class="form-control" @bind="data" />Question 17: What is the Event-Binding in Blazor?
Answer: Event binding is nothing but a way to call a handler function written in C# on a specific event, like on button click, text change, enter, or leaving the focus from a DOM element.
<button @onclick="@(()=>changeCity())">Click</button>Question 18: What are the life cycle methods of Blazor Components.
Answer:
The Blazor application provides different functions for specific tasks in the life cycle of Blazor components in the form of synchronous as well as asynchronous methods.
- OnInitialized
- OnInitializedAsync
- OnParametersSet
- OnParametersSetAsync
- OnAfterRender
- OnAfterRenderAsync
- ShouldRender
Question 19: When should I use Blazor Server?
Answer: Blazor allows us to create rich interactive UI to our .NET apps. For using Blazor Server there are many reasons:
- There is no need to rewrite existing app logic.
- when you want to offload work from the client to the server.
- Blazor Server apps require only a small download to establish the connection.
- It is a great solution for apps that need to run on low-powered devices.
Question 20: When should I use Blazor WASM?
Answer: Blazor allows us to create rich interactive UI to our .NET apps. For using Blazor WebAssembly there are many reasons:
- Blazor WebAssembly require Low latency Network
- No Need for JavaScript understandings for client-side interactions.
- Blazor WebAssembly apps allow Offline support.





