What is an Electromagnet?
An electromagnet, a piece made of metal that turns magnetic when an electrical current passes through it or close to it, is called. When the wire is wrapped in a loop, current passes through it to form these magnets. The coil's magnetic field is created when current flows through it. It forms a circular shape. Its density is highest at the center of the coil and it weakens as it moves away from the coil.

Iron is the most common conductor for the Electromagnet. It concentrates the current and makes high-power electromagnets. The electromagnet is superior to permanent magnets because we can adjust the current to control its durability and magnetic fields. Permanent magnets do not allow this.
Working Principle of Electromagnets
How do electromagnets actually work? Let's look at the iron nail. What is the reason it doesn't produce a magnet field when it's not being influenced by an electrical field?

Above is a picture of a coil wrapped around an iron nail. The iron nail by itself is not magnetic.
Normally, the atoms of the nail are oriented in random directions. However, individual magnetic fields can cancel out each other. These atoms can be reoriented by applying an electric current to point in the same direction. These magnetic fields create a strong magnetic force. This reorientation is a function of the current flow. As it increases, the magnetic field becomes stronger. The magnetic field created by increasing the current flow won't be affected if all particles are perfectly reoriented in the same direction. The magnet is considered saturated at this point.
Lines of force around an Electromagnet
The current that passes through the wire behaves as an electromagnet because of the magnetic field it creates around the conductor. The field is composed of two poles, the north and south. It begins at the north pole and ends at the south pole. The center of the loop is where the field strength is highest. The strength of the field decreases as the wire moves from the center.
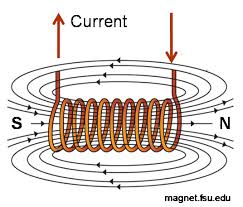
The field strength can be increased by winding more loops around the iron part. This shows that flux in conductors is directly proportional to the current flowing through them and the number of turns.
MMF = N
This equation shows that MMF stands for Magneto-motive force. N is the number or turns, and I is current in amperes.
The Electromagnet's Magnetic Strength
- The Electromagnet has 2 conductors. One is a wire loop, and the other is a conductor whose loop is wound.
- These conductors are subject to magnetic fields when current passes through them. The magnetic fields and these fields interact with one another and cause force to act on the conductors.
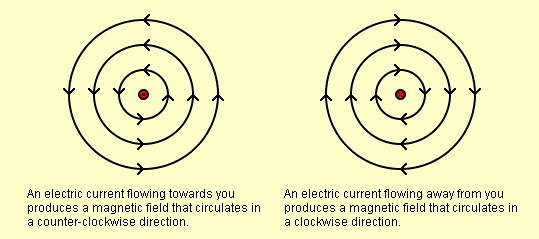
- The conductors that have the same current direction will attract each other. This is evident in the diagram.
- If the current direction is in the opposite direction, the field of 2 conductors becomes strong and repels each other.
Electromagnet's Advantages
- The electromagnet's most significant feature is its ability to vary its magnetic strength.
- The electromagnt works as an insulator if the current does not pass through its windings.
- A larger increase in the strength of the magnet is possible if the current is in large amperes.
- This allows for a variation in the strength and power of electromagnetic waves, making it useful in industries that require a different flux value.
Electromagnet's disadvantages
- They heat up quickly
- It uses a lot of energy
- Their magnetic field can hold huge amounts of energy. The energy will be released if the electric current is disrupted.
Electromagnet applications
The electromagnets are used in many areas, including at home, in industries and in medical equipment. These are just a few of the many applications.
- It is used in heavy machinery, such as factories, and small electronic instruments like motors.
- It was also used in experiments to produce the magnetic field.
- The solenoids are the electromagnets. They create the uniform magnetic field.
- It is used to produce the flux in the transformer. The core of the transformer acts like an electromagnet.
- It is used in various electrical relays.
- The electromagnet is also a key factor in the operation of the seminar's loudspeaker.
- The magnetic field can also be produced by medical resonance imaging machines.
- It is also used in VCR (videocassette recording) and tape recorders.
We hope that you find this article about the electromagnet helpful. We have covered everything related to it. Thank you for reading.





