What is WebRTC?
WebRTC
WebRTC stands for Web-based Real-Time Communication.
It is a free, open-source project that makes an application or a browser capable of communicating in real-time using Application Programming Interfaces a.k.a APIs. It allows interchanging audio, video, and other generic data between web pages or peers without using any extra plugins or applications.
Supported by various tech giants such as Apple, Google, Microsoft, Mozilla, and Opera, this technology is available on many browsers such as:
For PC: Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari, Opera. For telephonic devices: Android, Chrome OS, Firefox OS, Blueberry 10, IOS, and Tizen.

Origin:
Although Justin Uberti and Peter Thatcher are the original authors, Google was the firm which released WebRTC as an open-source project in May 2011, and standardization is looked after by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and World Wide Web Consortium (W3).
Then later in the same year, the Ericsson lab made the first implementation of WebRTC.
Working:
A WebRTC application follows a common application flow:
- Accessing the media devices that are to be sent or stream to the peer.
- Opening peer connections so that communication can be performed.
- Discovering peers for communication.
- Start streaming the media.
For creating a WebRTC application, following JavaScript APIs are to be used:
- getUserMedia() : To capture video and audio.
- MediaRecover: To record audio and video.
- RTCPeerConnection: To streams audio and video between users.
- RTCDataChannel: To stream data between the users.
- getStats: To retrieve a set of statistics about the WebRTC session.
Signalling:
To establish communications between peers, WebRTC uses RTCPeerConnection. After establishing the connection, it uses a mechanism called Signalling.
Signalling is the mechanism in which coordinate communication is used to send the control message. For example, If 1 peer is located on one server and another peer is on another server. So to communicate, WebRTC APIs will share the coordinates of the third mutually agreed server to both the servers so that they can communicate. For signalling, The Signalling server is used. The main role of the signalling server is to act as a bridge between the two peers with exposing minimum private information.
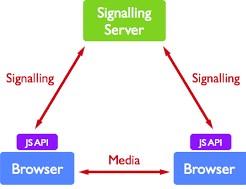
Session Description Protocol is the standard protocol which describes the peer to peer connection. It contains the codec, source, address and timing information of audio and video. After starting the signalling process, an offer is initiated by the user to initiate the call which includes a session description. This description is delivered to the user, then the callee will be called. The callee will respond to the offer with an answer message.
After this response ICE (Interactive Connectivity Establishment) framework is used to connect peers regardless of network topology.
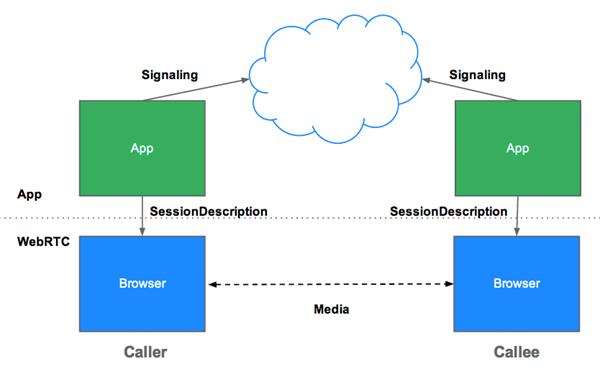
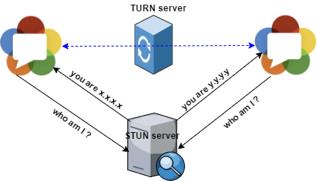
Once both the peers are mutually agreed on a compatible candidate, the candidate’s SDP is used by both the peers to create communication through which data flows. In case the Peer-peer connection fails, the WebRTC API’s uses STUN servers to get the IP address of the caller and TURN server to act as a relay server.
Security:
Encryption of all WebRTC components has been made mandatory, and one can only use the JavaScript APIs for secure origin. Signalling mechanism is not defined by WebRTC, so it depends on the user to choose the mechanism.





