What is Storage Area Network and Storage Protocols
Storage Area Network
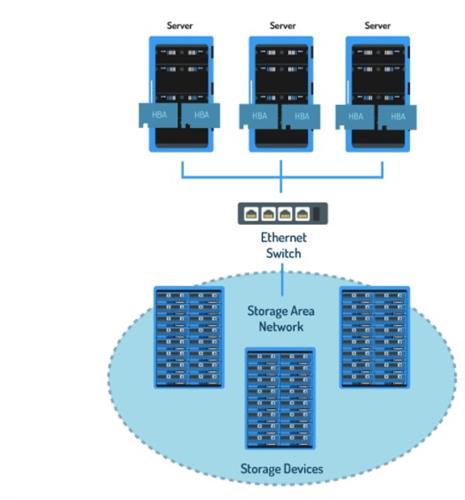
A data center built for a little business would be fine employing a DAS or a NAS since there are now devices that provide terabytes of capacity and more capacity are often added by simply installing additional NAS storage devices. However, if that business grew into an outsized enterprise, its servers would wish to accommodate tons more data than DAS and NAS could hold.
A SAN (Storage Area Network) is one or many block-level storage devices clustered together that are attached to a high-speed network that applications running on the servers, can hook up with so as to access the info. A characteristic of a SAN is that albeit the storage is in another physical location, to the server, it's and acts as if it had been attached as a DAS.
A SAN requires that servers trying to attach thereto even have certain protocols. Because a SAN requires a high-speed connection, faster protocols like iSCSI, Fiber Channel (FC), and more recently Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) are wont to transmit data at higher speeds on the TCP/IP network (internet).
This ability for storage to be shared outside of an area network makes a SAN an efficient storage type for larger companies whose employees got to access stored data from quite one location. Because a SAN requires higher speeds and a wider network area, it is often costlier to line up but the power to switch the dimensions of the storage from anywhere at any time, called scalability, outweighs the prices for giant organizations.
One way to know the difference between a NAS and a SAN is that NAS is storage that connects to a network, and a SAN may be a network of storage that servers can hook up with. Also, a NAS manages storage as a filing system directly while SAN storage devices don't, and it's the server’s OS that's liable for creating the storage filing system. this might not seem important from a user’s standpoint; however, it affects the speed at which data is processed since a tool that doesn't need to worry about filing its own data will run faster and be more efficient, which is vital for overall data center efficiency.
Storage Protocols
Many types of storage protocols are available for configuring data center storage. the foremost efficient protocol for a specific data center depends on factors like the dimensions of the info center, sorts of servers used, and available budget. for instance, some protocols ensure faster data transmission speeds but cost more to implement. Configuring storage with protocols that match the quantity of knowledge traffic a knowledge center wants to handle can increase efficiency and ensure data gets to customers.The following table lists common storage protocols and which storage configurations they're applied to:
|
Protocol |
Application |
|
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) |
Medium- sized blade servers, Enterprise servers, DAS |
|
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) |
Small-sized tower server, DAS |
|
eSATA (external SATA) |
Small-sized tower server, DAS |
|
SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) |
Medium-sized blade servers, Enterprise servers, DAS |
|
FC (Fiber Channel) (single-mode) (SMF) |
Enterprise servers, SAN |
|
FC (Fiber Channel) (multi-mode) (MMF) |
Enterprise servers, SAN |
|
FCoE (Fiber Channel over Ethernet) |
Enterprise servers, SAN |
|
iSCSI (internet Small Computer System Interface) |
Enterprise servers, NAS |




