What is Direct Attached Storage in Virtualization Concepts?
Direct Attached Storage
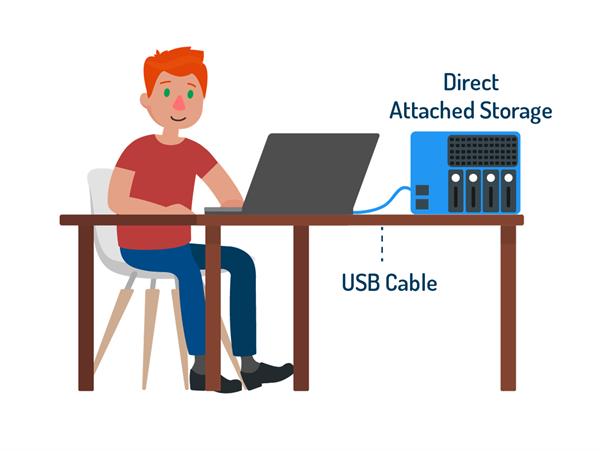
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) means that a physical storage device is directly attached to a server or personal computer. The hard drive of a laptop is a type of DAS because it fits the definition of a storage device directly attached to a personal computer. Supplementing a hard drive when more storage is needed with another DAS basically means plugging in an external storage device, like hooking up an external hard drive to a laptop to store media or work files.
The following are types of storage that can be used as DAS:
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) - Uses magnetic rotating disks to hold data, which is then read by a rotating arm that reads and writes the data onto the disk. Many personal computers have HDDs, or as they are usually referred to, “hard drives”.
- Solid State Drive (SSD) - Made out of a collection of electronic circuits (chips) that store and transmit data. Unlike hard disk drives, solid-state drives don’t have any moving parts like the arm of the HDD that has to rotate to find the right location on a disk. This means that SSDs are faster and more durable. Another benefit of SSDs is their efficiency, due to the fact that they don’t have any moving parts, so they require less energy to operate.
- Optical Disk Drive (ODD) - Uses lasers to read and write data onto optical disks. A good example of a type of media that uses an optical disk drive is a DVD player. Although most optical disks can only hold 50GB or less as opposed to the commonly available 256GB to 1TB (terabyte) HDDs and SSDs, ODDs are convenient because they are inexpensive and highly portable.
The types of storage mentioned above have different benefits, but each has the ability to store data and can be used as an external storage option. The direct-attached storage architecture is beneficial for personal use or for small businesses that need to purchase a set amount of data storage at a time, and it is simple enough not to need a significant IT management presence. The goal is to grow data storage in increments by simply adding additional drives when needed.
One of the caveats of adding more storage is that there are a lot of different brands and builds of storage devices, and they need to be compatible with the computing systems that are accessing them. In order to set up DAS, the storage device needs to have the correct technology employed so it can speak the same language as the server it’s attached to. This "language" is called a protocol. On a storage device, the protocol can be identified by the ports and outlets it uses. An example would be the USB (Universal Serial Bus) protocol, which can be identified by the USB ports and cables. Because storage devices come in various protocols, the server may need an adapter to communicate with the storage device so users can store and access data from it.
The protocol adapter for servers is called an HBA (host bus adapter). This is a piece of hardware, similar in appearance to a card with a port for a plug, which is plugged into a server and adapts the server to the storage device’s protocol (language). Once the HBA is attached to the server, and the cables with the right protocol are used, a storage device can be attached, allowing the DAS to now be able to talk to the server. The protocols most commonly used for DAS are SCSI, SATA, SAS, and USB. So, if a SCSI protocol HBA is attached to the server, and the HBA is connected to a SCSI storage device with cables, it will be able to transmit data from the server to the storage and vice versa.





