Exploring Software Testing
Aug 24, 2019
Software Testing,
6687 Views
in this article, we learn about the Software Testing
Software Testing
- Computer programs are designed and developed by human beings and hence are prone to errors.
- Unchecked, they can lead to a lot of problems, including social implications.
- Testing the software becomes an essential part of the software development lifecycle.
- Carrying out the testing activities for projects has to be practiced with proper planning and must be implemented correctly.
- “Testing is the process of executing a program with the intention of finding errors.” – Myers
- “Testing can show the presence of bugs but never their absence.” – Dijkstra

Most Common Software Problems
- Incorrect calculation
- Incorrect data edits & ineffective data edits
- Incorrect matching and merging of data
- Data searches that yield incorrect results
- Incorrect processing of data relationship
- Incorrect coding/implementation of business rules
- Inadequate software performance
- Confusing or misleading data
- Software usability by end users & Obsolete Software
- Inconsistent processing
- Unreliable results or performance
- Inadequate support of business needs
- Incorrect or inadequate interfaces with other systems
- Inadequate performance and security controls Incorrect file handling
Need of Software Testing
- Executing a program with the intent of finding an error.
- To check if the system meets the requirements and be executed successfully in the Intended environment.
- To check if the system is “ Fit for purpose”.
- To check if the system does what it is expected to do.
- A good test case is one that has a probability of finding an as-yet-undiscovered error.
- A successful test is one that uncovers a yet undiscovered error.
- A good test is not redundant.
- A good test should be “best of breed”.
- A good test should neither be too simple nor too complex.
Types of Software Testing
- Manual Testing
- Manual testing includes testing a software manually, i.e., without using any automated tool or any script.
- In this type, the tester takes over the role of an end-user and tests the software to identify any unexpected behavior or bug.
- There are different stages for manual testing such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing.
- Testers use test plans, test cases, or test scenarios to test software to ensure the completeness of testing.
- Manual testing also includes exploratory testing, as testers explore the software to identify errors in it.
- Automation Testing
- Automation testing, which is also known as Test Automation, is when the tester writes scripts and uses another software to test the product.
- This process involves the automation of a manual process.
- Automation Testing is used to re-run the test scenarios that were performed manually, quickly, and repeatedly.
Software Testing Methods
- Black Box Testing
- Incorrect or missing functions, Interface errors, Errors in data structures or external database access, Performance errors, Initialization and termination errors
- Black box / Functional testing
- Based on requirements and functionality
- Not based on any knowledge of internal design or code
- Covers all combined parts of a system
- Tests are data-driven
- Black Box Testing method is applicable to the following levels of software testing:
- Integration Testing
- System Testing
- Acceptance Testing
- Example: A tester, without knowledge of the internal structures of a website, tests the web pages by using a browser; providing inputs (clicks, keystrokes) and verifying the outputs against the expected outcome.

- White Box Testing
- Knowledge of the internal program design and code required.
- Tests are based on coverage of code statements, branches, paths, conditions.
- Incorrect or missing functions, Interface errors, Errors in data structures or external database access, Performance errors, Initialization and termination errors
- White box testing / Structural testing
- Based on the knowledge of the internal logic of an application's code
- Based on the coverage of code statements, branches, paths, conditions
- Tests are logically driven
- White Box Testing method is applicable to the following levels of software testing:
- Unit Testing: For testing paths within a unit.
- Integration Testing: For testing paths between units.
- System Testing: For testing paths between subsystems.
- Example: A tester, usually a developer as well, studies the implementation code of a certain field on a webpage, determines all legal (valid and invalid) AND illegal inputs and verifies the outputs against the expected outcomes, which is also determined by studying the implementation

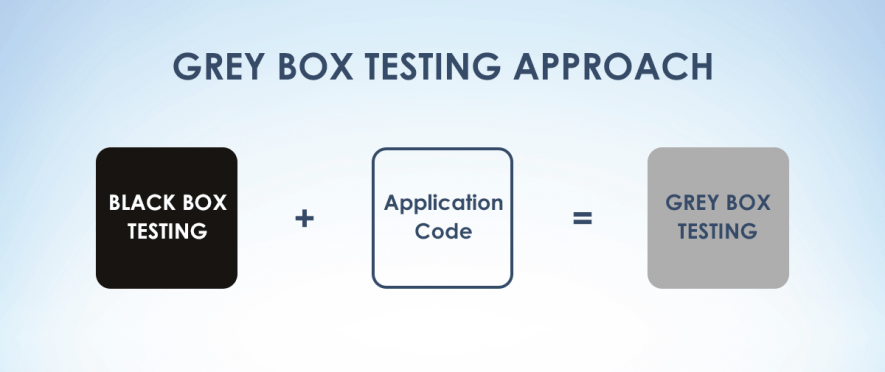
- Grey-Box Testing
- It combines the concept of both Black box as well as white box testing.
- In Grey box testing, the inside of your product is partly known to the tester.
- This has partial access to data-structures residing internally for designing different test cases, but at the same time tests from a user's perspective or like a black-box tester.
- Grey box testing has its name grey because from a tester's eye, it's like a semi-transparent box and also combining the color of black and white gives the shades of grey.
- Main features:
- test design is based on the data structures and algorithms knowledge
- actual tests are conducted using the exposed interfaces
- a tester can have access to the source code for test cases design
- Test design techniques based on grey box testing:
- matrix testing
- regression testing
- orthogonal array testing
- pattern testing
Levels of Software Testing
- Levels of testing include different methodologies that can be used while conducting software testing.
- The main levels of software testing are −
- Functional Testing
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- System Testing
- Regression Testing
- Acceptance Testing
- Alpha Testing
- Beta Testing
- Non-functional Testing
- Performance Testing
- Load Testing
- Stress Testing
- Usability Testing
- Security Testing
- Portability Testing





