What is AWS EBS ?
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) gives square level stockpiling volumes to use with EC2 occurrences. EBS volumes act like crude, unformatted square gadgets. You can mount these volumes as gadgets on your occasions. EBS volumes that are appended to a case are uncovered as capacity volumes that continue autonomously from the life of the case. You can make a document framework on the head of these volumes, or use them in any capacity you would utilize a square gadget, (for example, a hard drive). You can powerfully change the arrangement of a volume joined to an occasion.

Amazon EBS is suggested for information that must be rapidly available and requires long haul steadiness. EBS volumes are especially appropriate for use as the essential stockpiling for record frameworks, databases, or any applications that require fine granular updates and access to crude, unformatted, square level stockpiling. Amazon EBS is appropriate to both database-style applications that depend on irregular peruses and composes, and to throughput-concentrated applications that perform long, consistent peruses and composes.
You can look over four changed volume types to adjust the ideal cost and execution. You can accomplish single digit-millisecond inactivity for superior database outstanding burdens, for example, SAP HANA or gigabyte every second throughput for enormous, consecutive remaining burdens, for example, Hadoop. You can change volume types, tune execution, or increment volume size without disturbing your basic applications, so you have financially savvy stockpiling when you need it, Designed for mission-critical systems, EBS volumes are replicated within an Availability Zone (AZ) and can easily scale to petabytes of data. Also, you can use EBS Snapshots with automated lifecycle policies to back up your volumes in Amazon S3, while ensuring geographic protection of your data and business continuity.
Features:
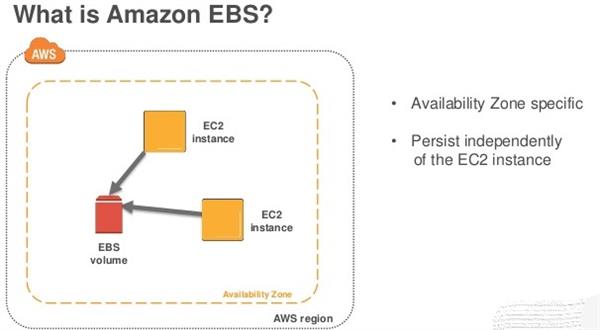
Amazon EBS permits you to make stockpiling volumes and append them to Amazon EC2 cases. When appended, you can make a document framework on the head of these volumes, run a database, or use them in some other way you would utilize square stockpiling. Amazon EBS volumes are put in a particular Availability Zone where they are consequently recreated to shield you from the disappointment of a solitary segment. All EBS volume types offer tough preview capacities and are intended for 99.999% accessibility.
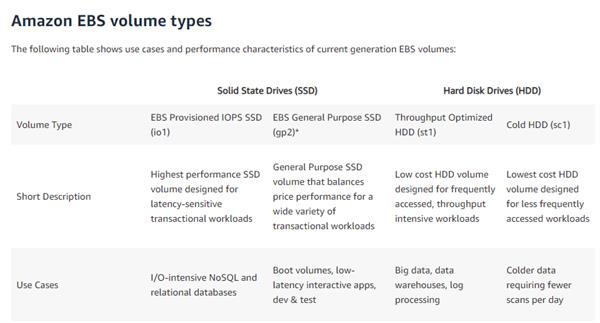
Amazon EBS gives a scope of alternatives that permit you to streamline capacity execution and cost for your remaining burden. These choices are isolated into two significant classes: SSD-backend capacity for value-based remaining burdens, for example, databases and boot volumes (execution relies basically upon IOPS), and HDD-sponsored capacity for throughput escalated outstanding tasks at hand, for example, MapReduce and log handling (execution relies principally upon MB/s).
SSD-supported volumes incorporate the best Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) for dormancy touchy value-based outstanding tasks at hand and General Purpose SSD (gp2) that parity cost and execution for a wide assortment of value-based information. HDD-backend volumes incorporate Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) for much of the time got to, throughput escalated outstanding tasks at hand, and the most reduced cost Cold HDD (sc1) for less every now and again got to information.
Versatile Volume is a component of Amazon EBS that permits you to progressively build limit, tune execution, and change the kind of live volumes with no personal time or execution sway. This permits you to handily right-estimate your organization and adjusts to execution changes.
EBS Volumes:
An Amazon EBS volume is a tough, square level stockpiling gadget that you can append to your occurrences. After you join a volume to a case, you can utilize it as you would utilize a physical hard drive. EBS volumes are adaptable. For current-age volumes joined to current-age occasion types, you can powerfully build size, adjust the provisioned IOPS limit, and change volume type on live creation volumes.
You can utilize EBS volumes as essential stockpiling for information that requires visit refreshes, for example, the framework drive for a case or capacity for a database application. You can connect numerous EBS volumes to a solitary case. The volume and occurrence must be in a similar Availability Zone. Contingent upon the volume and occasion types, you can utilize Multi-Attach to mount a volume to various examples simultaneously.
Advantages of utilizing EBS volumes
EBS volumes give benefits that are not given by case store volumes.
Information accessibility
At the point when you make an EBS volume, it is consequently imitated inside its Availability Zone to forestall information misfortune because of the disappointment of any single equipment part. You can join an EBS volume to an EC2 occasion in a similar Availability Zone. After you join a volume, it shows up as a local square gadget like a hard drive or another physical gadget. By then, the example can interface with the volume similarly as it would with a neighborhood drive. You can interface with the case and organization the EBS volume with a record framework, for example, ext3, and afterward introduce applications.
Information steadiness
An EBS volume is an off-example stockpiling that can persevere autonomously from the life of a case. You keep on paying for the volume utilized as long as the information endures.
EBS volumes that are joined to a running occasion can consequently withdraw from the case with their information flawless when the example is ended on the off chance that you uncheck the Delete on Termination checkbox when you arrange EBS volumes for your occurrence on the EC2 reassure. The volume would then be able to be reattached to another example, empowering speedy recuperation. On the off chance that the checkbox for Delete on Termination is checked, the volume(s) will erase upon the end of the EC2 example.
Information encryption
For rearranged information encryption, you can make encoded EBS volumes with the Amazon EBS encryption highlight. All EBS volume types bolster encryption. You can utilize encoded EBS volumes to meet a wide scope of information very still encryption prerequisites for managed/evaluated information and applications. Amazon EBS encryption utilizes 256-piece Advanced Encryption Standard calculations (AES-256) and an Amazon-oversaw key foundation.
Types of Volumes
SSD-backend volumes (IOPS-serious)
Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) volumes
IO1 is backend by strong state drives (SSDs) and is the best EBS stockpiling alternative intended for basic, I/O concentrated database and application outstanding tasks at hand, just as throughput-serious database and information distribution center remaining burdens, for example, HBase, Vertica, and Cassandra. These volumes are perfect for the two IOPS-concentrated and throughput-serious outstanding tasks at hand that require incredibly low inactivity.
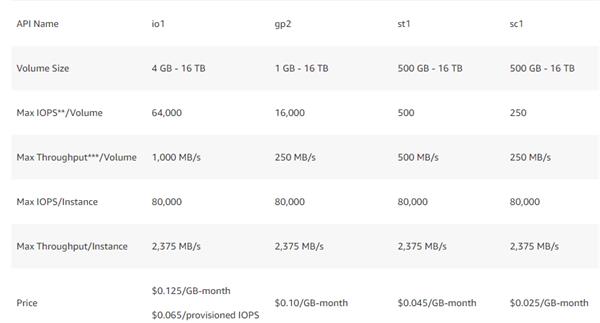
IO1 is intended to convey a steady gauge execution of up to 50 IOPS/GB to a limit of 64,000 IOPS and give up to 1,000 MB/s of throughput per volume1. To expand the advantage of io1, we suggest utilizing EBS-streamlined EC2 occurrences. At the point when appended to EBS-streamlined EC2 occasions, io1 is intended to accomplish single-digit millisecond latencies and is intended to convey the provisioned presentation 99.9% of the time. For more data about occurrence types that can be propelled as EBS-improved examples, see Amazon EC2 Instance Types. For more data about Amazon EBS execution rules, see Increasing EBS Performance.
1To accomplish the constraint of 64,000 IOPS and 1,000 MB/s throughput, the volume must be joined to a Nitro framework EC2 occurrence.
Broadly useful SSD (gp2) volumes
GP2 is the default EBS volume type for Amazon EC2 examples. These volumes are backend by strong state drives (SSDs) and are appropriate for an expansive scope of value-based outstanding tasks at hand, including dev/test situations, low-dormancy intuitive applications, and boot volumes. GP2 is intended to offer single-digit millisecond latencies, convey a predictable standard execution of 3 IOPS/GB (least 100 IOPS) to a limit of 16,000 IOPS, and give up to 250 MB/s of throughput per volume. GP2 volumes littler than 1 TB can likewise blast up to 3,000 IOPS. I/O is remembered for the cost of gp2, so you pay just for every GB of capacity your arrangement. GP2 is intended to convey the provisioned exhibition 99% of the time. In the event that you need a more noteworthy number of IOPS than gp2 can give, or on the off chance that you have an outstanding task at hand where low inertness is basic or you need better execution consistency, we suggest that you use io1. To amplify the exhibition of gp2, we suggest utilizing EBS-advanced EC2 occurrences.
HDD-supported volumes (MB/s-serious)
Throughput enhanced HDD (st1) volumes
ST1 is supported by hard plate drives (HDDs) and is perfect for as often as possible got to, throughput escalated outstanding tasks at hand with huge datasets and huge I/O sizes, for example, MapReduce, Kafka, log handling, information distribution center, and ETL remaining tasks at hand. These volumes convey execution as far as throughput, estimated in MB/s, and incorporate the capacity to blast up to 250 MB/s per TB, with a pattern throughput of 40 MB/s per TB and a most extreme throughput of 500 MB/s per volume. ST1 is intended to convey the normal throughput execution 99% of the time and has enough I/O credits to help a full-volume examine at the burst rate. To augment the presentation of st1, we suggest utilizing EBS-enhanced EC2 occasions.
Cold HDD (sc1) volumes
SC1 is sponsored by hard circle drives (HDDs) and gives the most minimal expense per GB of all EBS volume types. It is perfect for less much of the time to get to outstanding tasks at hand with enormous, cold datasets. Like st1, sc1 gives a burst model: these volumes can blast up to 80 MB/s per TB, with a benchmark throughput of 12 MB/s per TB and the greatest throughput of 250 MB/s per volume. For inconsistently got to information, sc1 gives incredibly cheap capacity. SC1 is intended to convey the normal throughput execution 99% of the time and has enough I/O credits to help a full-volume check at the burst rate. To amplify the exhibition of sc1, we suggest utilizing EBS-enhanced EC2 examples.
Amazon EBS snapshots
You can back up the information on your Amazon EBS volumes to Amazon S3 by taking point-in-time previews. Previews are steady reinforcements, which implies that solitary the squares on the gadget that have changed after your latest depiction are spared. This limits the time required to make the preview and saves money on capacity costs by not copying information. At the point when you erase a preview, just the information special to that depiction is expelled. Every preview contains the entirety of the data that is expected to reestablish your information (from the second when the depiction was taken) to another EBS volume.
At the point when you make an EBS volume dependent on a depiction, the new volume starts as a careful imitation of the first volume that was utilized to make the preview. The reproduced volume loads information out of sight with the goal that you can start utilizing it right away. In the event that you get to the information that hasn't been stacked at this point, the volume promptly downloads the mentioned information from Amazon S3, and afterward keeps stacking the remainder of the volume's information out of sight.
Multi-volume Snapshots
Previews can be utilized to make a reinforcement of basic remaining burdens, for example, a huge database or a record framework that ranges over different EBS volumes. Multi-volume depictions permit you to take definite point-in-time, information facilitated, and crash-reliable previews over different EBS volumes joined to an EC2 occasion. You are not, at this point required to stop your occasion or to arrange between volumes to guarantee crash consistency since previews are naturally taken over various EBS volumes.
How incremental snapshots work
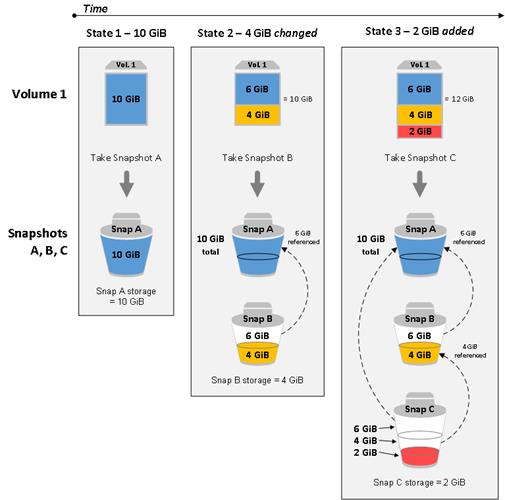
This segment gives delineations of how an EBS preview catches the condition of a volume at a point in time, and furthermore how progressive depictions of a changing volume make a past filled with those changes.
In the graph underneath, Volume 1 has appeared at three focuses on time. A preview is taken off every one of these three-volume states.
In-State 1, the volume has 10 GiB of information. Since Snap An is the principal depiction taken of the volume, the whole 10 GiB of information must be duplicated.
In-State 2, the volume despite everything contains 10 GiB of information, yet 4 GiB have changed. Snap B needs to duplicate and store just the 4 GiB that changed after Snap A was taken. The other 6 GiB of unaltered information, which are now duplicated and put away in Snap An, are referenced by Snap B as opposed to (once more) replicated. This is shown by the ran bolt.
In-State 3, 2 GiB of information has been added to the volume, for a sum of 12 GiB. Snap C needs to duplicate the 2 GiB that was included after Snap B was taken. As appeared by the ran bolts, Snap C likewise references 4 GiB of information put away in Snap B, and 6 GiB of information put away in Snap A.
The all-out capacity required for the three previews is 16 GiB.
Relations among numerous previews of a volume.
Amazon EBS encryption
Use Amazon EBS encryption as a straight-forward encryption answer for your EBS assets related to your EC2 cases. With Amazon EBS encryption, you aren't required to manufacture, keep up, and secure your own key administration framework. Amazon EBS encryption utilizes AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) client ace keys (CMK) when making scrambled volumes and depictions.
Encryption tasks happen on the servers that have EC2 occurrences, guaranteeing the security of the two information very still and information in-travel between an example and its connected EBS stockpiling.
How EBS encryption functions You can encode both the boot and information volumes of an EC2 example. At the point when you make a scrambled EBS volume and join it to a bolstered example type, the accompanying sorts of information are encoded:
Information very still inside the volume.
All information moving between the volume and the occasion.
All previews made from the volume.
All volumes made from those previews.
EBS scrambles your volume with an information key utilizing the business standard AES-256 calculation. Your information key is put away on-circle with your encoded information, yet not before EBS scrambles it with your CMK. Your information key never shows up on the plate in plaintext. A similar information key is shared by depictions of the volume and any ensuing volumes made from those previews.
Amazon EBS– optimized instances
An Amazon EBS–advanced occurrence utilizes an enhanced design stack and gives extra, committed limit with regards to Amazon EBS I/O. This enhancement gives the best execution to your EBS volumes by limiting conflict between Amazon EBS I/O and other traffic from your occurrence.
EBS–improved occurrences convey committed transfer speed to Amazon EBS. At the point when joined to an EBS–upgraded example, General Purpose SSD (gp2) volumes are intended to convey their standard and burst execution 99% of the time, and Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) volumes are intended to convey their provisioned presentation 99.9% of the time. Both Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) and Cold HDD (sc1) ensure execution consistency of 90% of burst throughput 99% of the time. Rebellious periods are around consistently disseminated, focusing on 99% of expected all-out throughput every hour.
So Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) gives square level stockpiling volumes to use with EC2 occurrences. EBS volumes act like crude, unformatted square gadgets. You can mount these volumes as gadgets on your occasions. EBS volumes that are appended to a case are uncovered as capacity volumes that continue autonomously from the life of the case. You can make a document framework on the head of these volumes, or use them in any capacity you would utilize a square gadget, (for example, a hard drive). You can powerfully change the arrangement of a volume joined to an occasion.