Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a substance whose resistivity lies between the conductors and insulators as shown in above figure. Some properties associated with semiconductor are as follows.
• The resistivity of semiconductor lies between insulators and conductors i.e. more than insulator and less than a conductor.
• Semiconductors have a negative temperature coefficient. The resistance in semiconductors increases with the decrease in temperature and vice versa.
• The Conducting properties of Semiconductor can be changed by adding suitable metallic impurity, which is the very important property of semiconductor which provides a base of the electronics industry.
Classification of semiconductors.
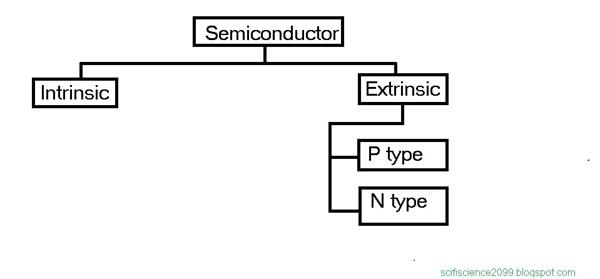
Intrinsic Semiconductors
A Semiconductor in its pure form is term as an intrinsic semiconductor. The properties of an intrinsic semiconductor are following
• The electrons and holes are purely created by thermal excitation.
• The number of free electrons and the number of holes are equal.
• The conduction capability is low at room temperature
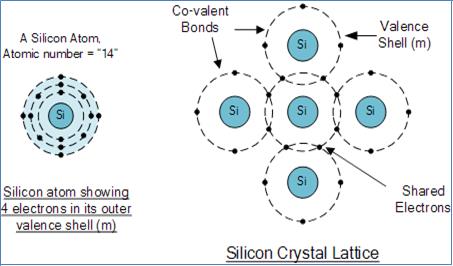
The most used material in the semiconductor industry is silicon. Silicon has four valence electrons in its outermost shell shared with its nearest silicon atoms to form full orbitals of eight Electrons. The bond structure between the two silicon atoms is such that each atom shares one electron with its neighbor which make it bond very strong and stable. Crystals of pure silicon (or germanium) are therefore good insulators because of very few free electrons available to move around the silicon crystal, very high-value resistors. These silicon atoms are arranged in symmetrical pattern making them a crystalline solid structure. Pure silica crystal is generally said to be an intrinsic crystal and it has no impurities and therefore has no free electrons.
A Silicon Atom Structure
Pure crystal of Silicon.
The conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor can be increased by adding some impurities. This process of adding impurities in intrinsic materials is called as Doping. A doped semiconductor is called as an Extrinsic Semiconductor. The impurities added, are mostly pentavalent and trivalent impurities.
Pentavalent Impurities
• The pentavalent impurities having five valence electrons in the outer most shell Example: Bismuth, Antimony, Arsenic, and Phosphorus. This is called as a donor atom because it donates one electron to the conduction band of pure semiconductor atom.
Trivalent Impurities The trivalent impurities having three valence electrons in the outer most shell. Example: Gallium, Indium, Aluminum, Boron. This is called an acceptor atom because it accepts one electron from the semiconductor atom.
Extrinsic Semiconductors
A semiconductor formed by doping a pure semiconductor is term as an extrinsic semiconductor. They are classified as N-type extrinsic semiconductor and P-Type extrinsic semiconductor depends upon the type of doping.



